ICS3U Python Mathematical Calculations
ICS3U Learning Goals
In this ICS3U Grade 11 Computer Science lesson you will be learning how to
- Perform basic mathematical calculations using variables (+ – * /) including powers, roots, and trigonometry
- Round the value of variables to a certain # of decimal places
- Generate random numbers to be used in your programs
Basic Python Math Operators
Now that you have learned how to store data in variables, you need to learn how to manipulate that data
Basic Operators in Python
A mathematical operator is an instruction that tells you what to do with two or more numbers. You have been using operators in math since you started school:
- Addition +
- Subtraction –
- Multiplication *
- Division /
In python, calculations are performed from left to right and will follow the rules of BEDMAS
If you need to use brackets in your formulas you must use ( ) and not [ ] or { }
Performing Calculations
In order to do a mathematical calculation, you perform the calculation and then assign the result of the calculation to a variable.
For example:
answer = 2*(x+y)
- The formula you are calculating goes on the right side of the equal sign and the variable you want to store that value in on the left.
- When the program executes it evaluates the right side (substituting the values for any other variables you have used) and then stores the result in the left side variable.
- You can use that variable any way you wish afterwards.
ICS3U Interactive Learning Activity - Grade 11 Computer Science
Let’s say you wanted to write a program that asks the user for 3 numbers and then outputs the average of those numbers
Type the following code into the Python Editor. It is only partially complete.
num1 = int(input("Enter a number: "))
num2 = int(input("Enter a number: "))
num3 = int(input("Enter a number: "))
result = _______________
print(result)
- Fill in the blanks to make the program function as expected
- Check to see if the output makes sense based on what you entered. Use your regular calculator to verify or check with my output
num1 = int(input("Enter a number: "))
num2 = int(input("Enter a number: "))
num3 = int(input("Enter a number: "))
result = (num1 + num2 + num3)/3
print(result)
ICS3U Interactive Learning Activity - Grade 11 Computer Science
Let’s say you wanted to write a program to calculate the Voltage across an electrical device. According to Ohm’s law in circuit analysis. You can figure out the voltage drop across a load using the formula
$$ Voltage = (Current)(Resistance) $$
Type the following code into the Python Editor. It is only partially complete.
current = float(input("Enter the current: "))
resistance = float(input("Enter the resistance: "))
voltage = ________________
print(voltage)
- Fill in the blanks to make the program function as expected
- Check to see if the output makes sense based on what you entered. Use your regular calculator to verify or check with my output
current = float(input("Enter the current: "))
resistance = float(input("Enter the resistance: "))
voltage = current * resistance
print(voltage)
ICS3U Interactive Learning Activity - Grade 11 Computer Science
Suppose you wanted to write a program that calculated the surface area and volume of a rectangular prism. You will need to apply these formulas
$$ SA = 2wl + 2wh + 2lh $$
$$ V = lwh $$
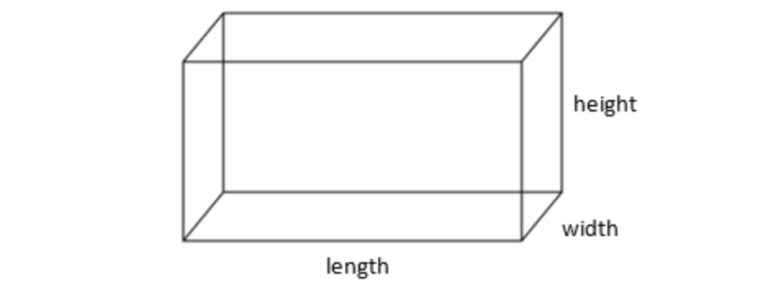
Type the following code into the Python Editor. It is only partially complete.
length = float(input("Enter the length of the prism: "))
width = float(input("Enter the width of the prism: "))
height = float(input("Enter the height of the prism: "))
surfaceArea = _____________________
volume = _____________________
print("The surface area of the prism is: ", surfaceArea)
print("The volume is: ", volume)
- Fill in the blanks to make the program function as expected
- Check to see if the output makes sense based on what you entered. Use your regular calculator to verify or check with my output
length = float(input("Enter the length of the prism: "))
width = float(input("Enter the width of the prism: "))
height = float(input("Enter the height of the prism: "))
surfaceArea = 2*width * length + 2*width * height + 2*length*height
volume = length*width*height
print("The surface area of the prism is: ", surfaceArea)
print("The volume is: ", volume)
ICS3U Interactive Learning Activity - Grade 11 Computer Science
Suppose you wanted to write a program that calculated the tax of a restaurant bill. Assuming a tax rate of 13%
Type the following code into the Python Editor. It is only partially complete.
subtotal = float(input("Enter the subtotal of your bill: "))
tax = ______________
finaltotal = ______________
print("Bill:")
print("Subtotal: $",subtotal)
print("Tax: $", tax)
print("Total: $:", finaltotal)
- Fill in the blanks to make the program function as expected
- Check to see if the output makes sense based on what you entered. Use your regular calculator to verify or check with my output
subtotal = float(input("Enter the subtotal of your bill: "))
tax = subtotal * 0.13
finaltotal = subtotal + tax
print("Bill:")
print("Subtotal: $",subtotal)
print("Tax: $", tax)
print("Total: $:", finaltotal)
Types of Division in Python
There are 3 ways you can deal with the division of numbers in python
- Normal Division / This tells you the decimal equivalent
- Integer Division // This tells you the whole number part of the division
- Modulus Division % This tells you the integer remainder portion of the division
ICS3U Interactive Learning Activity - Grade 11 Computer Science
Type the following code into the Python Editor.
x = int(input("Enter a number: "))
y = int(input("Enter a number: "))
print(x/y)
print(x//y)
print(x%y)
- Run the program by entering x= 27 and y = 4
- Run the program by entering x = 14 and y = 3
- Try to make sense of the outputs
Using inputs as 27 and 4 then
- 27/4 = 6.75 as you would see on a calculator
- 27//4 = 6 because this is the integer part of 6.75
- 27%4 = 3 because 6*4 = 24 and 27 – 24 = 3 (the remainder)
Using inputs as 14 and 3 then
- 14/3 = 4.66666667 as you would see on a calculator
- 14//3 = 4 because this is the integer part of 4.66666667
- 14%3 = 2 because 4*3 = 12 and 14 – 12 = 2 (the remainder)
The % operator is a really good way to determine if a value is divisible by another value because the remainder of that division will be 0
Video Summary
Watch a video of your teacher summarizing the learning content for this section
Rounding and Random Numbers in Python
Rounding Numbers in Python
You probably have noticed that python displays a lot of decimal places when doing calculations. You can use the round function to help control that in your program
round()
Rounding Outputs But NOT Changing the value
This example will round a number when printing, but it keeps the precision for later calculations if you need to. The number in the brackets of the round function is used to control the number of decimal spots. So in the example below that would round to 2 decimal spots.
decimal1 = 75.36849382
print(round(decimal1,2))
Rounding by Changing the Actual Value
If you actually wanted to round a number in your program and lose some of the precision of the original number you just need to assign the result of the round function back to your original variable. This example would reduce to the precision of the variable to 1 decimal place.
decimal1 = 75.36849382
decimal1 = round(decimal1,1)
Random Values
It might be beneficial to you at some point to create a random number (Think dice games or times when you don’t want to enter test data from the keyboard).
You need to import the random library and then use the some of the different functions inside it.
import random
To generate random integers in the range of [a,b] you are going to use:
random.randint(a,b)
To generate random floating point values in the range [a,b] you are going to use:
random.uniform(a,b)
ICS3U Interactive Learning Activity - Grade 11 Computer Science
Here is a program that will generate some random values in between a particular range
Type the following code into the Python Editor.
import random
num1 = random.randint(0, 20)
num2 = random.uniform(15, 20)
print("The two random values are: ", num1, "and", num2)
- Run the code MANY times and see how it is generating the random values
For more information and list of other functions inside the random module check out this website
Video Summary
Watch a video of your teacher summarizing the learning content for this section
Advanced Math Topics in Python
Evaluating Exponents using Python
There are several different ways you can accomplish evaluating a power in python.
$$ power = base^{exponet}$$
The first is the easiest and it uses a ** operator
power = base**exponent
The second way requires a function in the math module. Just like when you were creating random numbers before, you must import this module before using any of the functions inside it.
import math
The function to calculate exponents is the pow function, and you must send two values of to that function to make it work. The base of the power you are calculating must be first, and then the exponent you are using is second.
power = math.pow(base,exponent)
There isn’t much difference between the two methods.
- ** is “faster” but you would never notice the difference when the program was running.
- pow will always generate the answer as a floating point value, where ** it depends on the data types of what values where used.
ICS3U Interactive Learning Activity - Grade 11 Computer Science
Here is a program that shows some examples of using the ** operator vs the pow function in the math library
Type the following code into the Python Editor.
import math
print(2**3)
print(2**3.0)
print(2.0**3)
print(math.pow(2,3))
print(math.pow(2,3.0))
print(math.pow(2.0,3))
- Run the code and observe the difference between the outputs
The ** operator will return an integer result if both values were integers. If any of the values were floating points, it will return a floating point answer
The pow function will always return a floating point answer regardless of the data types of its inputs
Square Root Functions in Python
In order to perform a square root in python you must also import the math library and then use its sqrt function
math.sqrt()
The value you want to take the square root of should go inside the brackets
radical = math.sqrt(radicand)
ICS3U Interactive Learning Activity - Grade 11 Computer Science
Here is a program that shows how the square root function behaves in python
Type the following code into the Python Editor.
import math
x = int(input("Enter a value: "))
result = math.sqrt(x)
print(result)
- Run the code with the following inputs x = 5, x = 4, x = -5
The sqrt function will always return a decimal number even if you would expect an integer with the x = 4 input
The function can’t handle a negative input and gives a runtime error when the program executes.
Trigonometry in Python
An issue with doing trigonometry in computer science in grade 11 is that you are likely used to working with angles using degrees as the unit. There is a different unit of measurement called radian measure that is used in engineering, computer science, and advanced level mathematics, but you aren’t introduced to that unit until grade 12 math.
Unfortunately, python requires the unit to be in radian measure in order to do all the calculations.
Radian Measure
Radian measure is just a different unit of measurement. There are 360 degrees in a circle. That was somebody’s arbitrary choice. Somebody else thought that since a circle is defined by its radius, a better way to describe angles in a circle would be to measure it like this
Define 1 radian of measurement to be the angle formed by travelling an arc length of length r. Since the circumference of a full circle is 2πr, you need 2π arc lengths of length r to fill the whole circle.
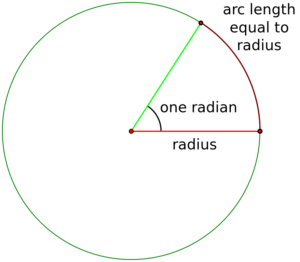
So comparing 360 degrees in a circle to 2π radians in a circle, gives that 1 radian is approximately 57.3 degrees.
Fortunately python has functions in its math library that does the conversions for you.
math.degrees(angle) #Converts radians to degrees
math.radians(angle) #Converts degrees to radians
With trigonometry we are typically interested in either finding side lengths of triangles or finding angles in triangles.
To do this you need to be able to find the sine, cosine, tangent of an angle or use their inverse functions to find angles. The inverse functions in programming are typically called arc functions: arcsin, arccos, arctan.
#Finding Ratios of Angles in Radians
math.sin(angle)
math.cos(angle)
math.tan(angle)
#Finding Angles in Radians
math.asin(ratio)
math.acos(ratio)
math.atan(ratio)
ICS3U Interactive Learning Activity - Grade 11 Computer Science
This example just asks the user to enter in an angle and the program will output all 3 of the primary trig ratios.
Type the following code into the Python Editor.
import math
angle = int(input("Enter a number:"))
s = math.sin(math.radians(angle))
c = math.cos(math.radians(angle))
t = math.tan(math.radians(angle))
print("sin(",angle,")=",round(s,3))
print("cos(",angle,")=",round(c,3))
print("tan(",angle,")=",round(t,3))
- Run the code with the following inputs angle = 30 and angle = 45 and angle = 60
- Check the answers using your calculator
The angle must be converted to radians before being put into the trig ratio. You will notice that I do the conversion to radians directly inside the the sine, cosine, and tangent functions, but you could do it outside and store it in its own variable and then put that variable inside the trig function
ICS3U Interactive Learning Activity - Grade 11 Computer Science
Suppose you wanted to write a program that helped students find all the angles inside a right angle triangle that were given all 3 sides.
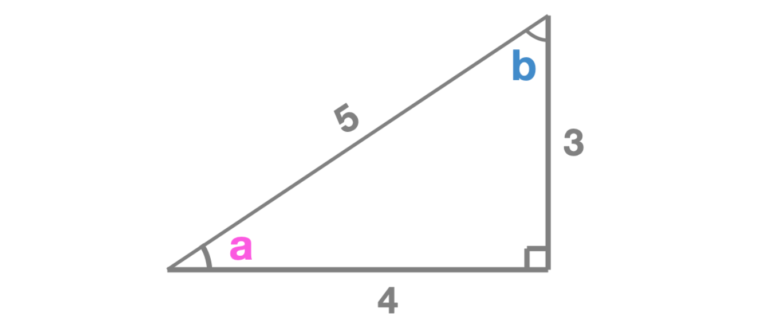
Type the following code into the Python Editor. It is only partially complete.
import math
a = math.__________(math.________(3/5))
b = math.__________(math.atan(___/___))
print("Angle a: ", round(a,1))
print("Angle b: ", round(b,1))
- Fill in the blanks to make the program function as expected
- Check to see if the output makes sense based on what you entered. Use your regular calculator to verify or check with my output
import math
a = math.degrees(math.asin(3/5))
b = math.degrees(math.atan(4/3))
print("Angle a: ", round(a,1))
print("Angle b: ", round(b,1))
Video Summary
Watch a video of your teacher summarizing the learning content for this section
ICS3U Coding Questions
Try to code the following questions using an IDE of your choice (Spyder, IDLE, Pycharm, etc). You will save those files on your computer for future reference.
Each question has:
- A video of your teacher live coding and explaining the solution
- The final code used in the video.
Try your best to solve the problems yourself without looking at the solutions.
Make sure you test your programs with multiple different inputs to ensure it is functioning properly.
ICS3U Practice Question
Name Your File: “ICS3Ucircle.py”
Write a program that asks the user for the radius of a circle and then calculates and displays both the area and the circumference of the circle.
$$ A = \pi r^{2} $$
$$ C = 2 \pi r $$
r = int(input("Enter the radius of the circle: "))
area = 3.14*r**2
circumference = 2*3.14*r
print("The area of a circle with radius",r,"is",area)
print("The circumference of a circle with radius",r,"is",circumference)
ICS3U Practice Question
Name Your File: “ICS3Utemperature.py”
Write a program that generates a random number that represents the temperature in Fahrenheit and converts it to degrees Celcius.
$$ C = \frac{5}{9} (F - 32) $$
Display both the random # and the temperature in a nicely formatted message. Round the answers to the nearest decimal. Check the calculations you get from the program with your calculator to make sure you are correct. Test with several values.
import random
f = random.randint(0,100)
c = (5/9)*(f-32)
print(f,"Fahrenheit =",round(c,1),"Celcius")
ICS3U Practice Question
Name Your File: “ICS3UfutureValue.py”
Write a program that can calculate how much money you earn on an investment. Ask the user for the initial investment, the interest rate per year, and the # of years. Output the total amount the investment will be worth and how much interest was earned.
$$ Amount = Investment ( 1 + rate)^{time} $$
Note: The interest rate needs to be converted to a decimal.
investment = float(input("Enter initial investment: "))
rate = float(input("Enter the % interest: "))
time = int(input("Enter number of years to invest: "))
amount = investment * (1 + rate / 100)**time
interest = amount - investment
print("Your investment is know worth: $",round(amount, 2))
print("You made $", round(interest,2), "in interest")
ICS3U Practice Question
Name Your File: “ICS3UtriangleSolved.py”
Write a program that asks the user to enter the two sides of a right angle triangle (not the hypotenuse) and then outputs the hypotenuse and the two interior angles of the triangle. Angles can be displayed to the nearest degree and the hypotenuse to one decimal place.
Here are the formulas you might need to accomplish this task.
$$ c^{2} = a^{2} + b^{2} $$
$$ \theta = tan^{-1}(\frac{opposite}{adjacent}) $$
Check the calculations you get from the program with your calculator to make sure you are correct. Check with several values.
import math
a = int(input("Enter side 1 of the right triangle: "))
b = int(input("Enter side 2 of the right triangle: "))
c = math.sqrt(a**2+b**2)
angle1 = math.degrees(math.atan(a/b))
angle2 = 90 - angle1
print("The hypotenuse is:",round(c,1))
print("The angles are:",round(angle1,0),"",round(angle2,0))
